Last Updated on April 28, 2025
The C1232 code points to a specific issue with the left front wheel speed sensor circuit in a vehicle. This sensor is vital for both measuring vehicle speed and ensuring the Anti-lock Braking System (ABS) operates correctly. When this component fails, it can severely impact driving safety and performance. A faulty wheel speed sensor can cause uneven wheel speeds, leading to poor vehicle control, loss of traction, and compromised braking. To maintain smooth and safe driving, it is crucial to diagnose and repair C1232-related problems promptly. Using an OBD-II scanner can help identify this fault early, preventing further complications.
What Causes the C1232 Error Code?
Understanding what causes the C1232 code helps in addressing it effectively. Typically, the problem lies with the left front wheel’s sensor, wiring, or associated systems. Issues such as corrosion, faulty wiring, misaligned sensors, and ABS module faults are common triggers. Poor maintenance practices, exposure to harsh environments, and normal wear and tear can also contribute. A proper diagnostic scan can reveal the exact root cause, allowing for timely and targeted repairs.
Detailed Causes of the C1232 Code
Let’s delve deeper into the primary causes of the C1232 error code:
1. Faulty Wheel Speed Sensor
The wheel speed sensor plays a key role in monitoring wheel rotation. If this sensor fails, it sends incorrect or no signals to the ABS system. Dirt, moisture, physical damage, or internal electrical failures can render the sensor ineffective, triggering the C1232 code. Regular inspection and cleaning can help prevent sensor failures.
2. Damaged or Corroded Wiring
The sensor is connected to the vehicle’s ABS module through wiring harnesses. Over time, exposure to road debris, moisture, and salt can corrode or damage these wires. A broken or short-circuited wire disrupts signal transmission, causing the system to log the C1232 error. Visual inspection often reveals obvious damage.
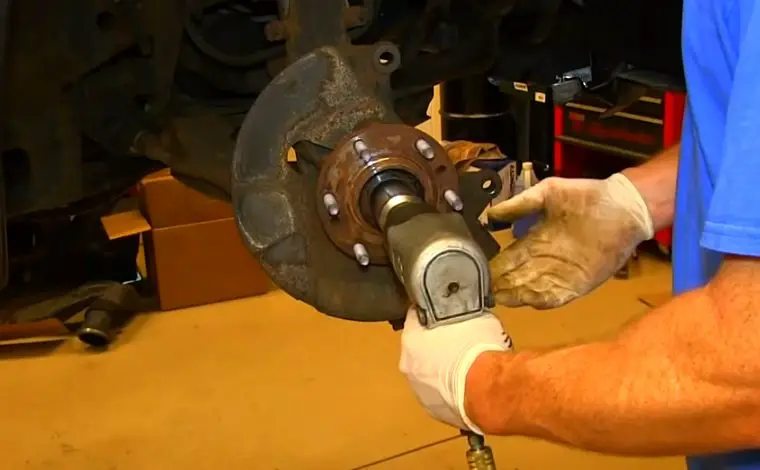

3. Poor Electrical Connections
Even if the wiring is intact, loose or oxidized connectors can impair communication between the sensor and the ABS module. Electrical continuity issues, due to aging connectors or dirt buildup, result in intermittent or failed signals, triggering warning lights and error codes.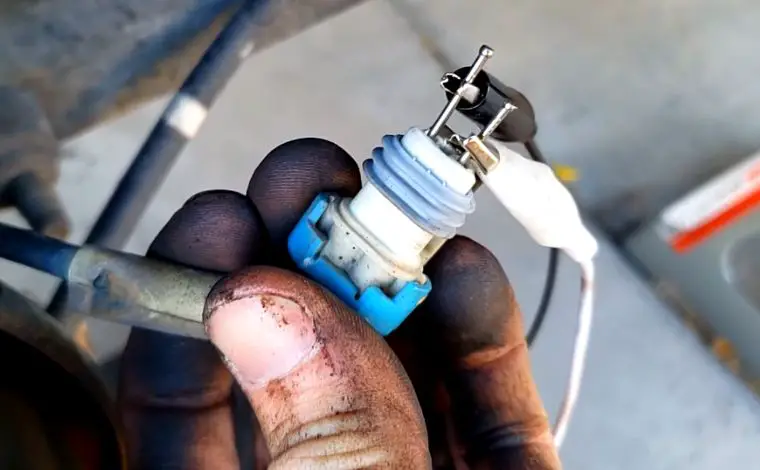
4. Damaged or Rusty Tone Ring
The tone ring, often attached to the wheel hub or axle, provides reference points for the sensor to calculate wheel speed. A broken, cracked, or rusty tone ring can mislead the sensor, causing inaccurate readings. In turn, this discrepancy will lead to a C1232 fault code.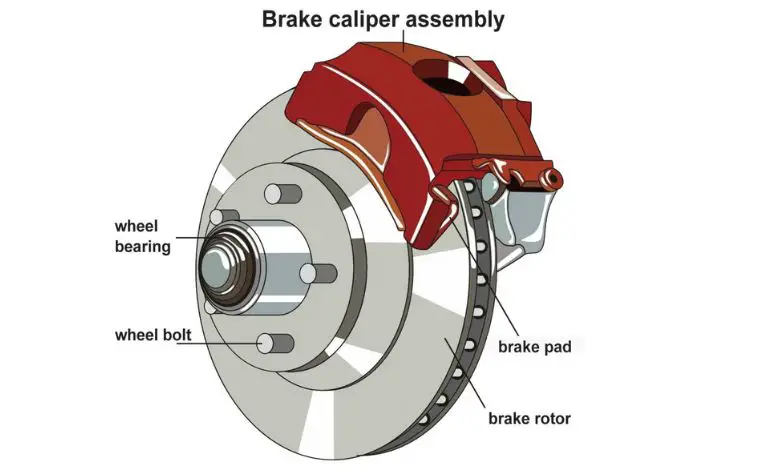
5. Faulty ABS Control Module
The ABS control module processes signals from all wheel speed sensors. A malfunctioning module might misinterpret good sensor signals as faulty or fail to recognize sensor inputs altogether. While rare, an ABS module failure is a critical and expensive cause of the C1232 code.
6. Sensor Misalignment
Proper alignment between the wheel speed sensor and the tone ring is essential. If the sensor gets misaligned due to impacts, suspension work, or wear, it may produce weak or erroneous signals. Correct alignment is necessary for optimal sensor performance and accurate speed readings.
7. Tire Size Discrepancy
Using tires of different sizes on a vehicle can confuse the ABS system. The wheels rotate at different speeds, and the system might interpret this as a fault, setting off codes like C1232. Always ensure uniform tire sizes and correct inflation across all wheels.
8. Faulty Wheel Bearing
The wheel bearing supports smooth wheel rotation. When a bearing is worn or loose, it can cause excessive wheel movement or vibrations, disrupting the wheel speed sensor’s signal. As a result, the ABS module may record a C1232 fault.
Symptoms of the C1232 Code
Recognizing symptoms early can prevent further vehicle damage and ensure driver safety. Here are the main indicators of a C1232 error:
1. ABS Warning Light Illuminates
The ABS light on your dashboard turns on as soon as the system detects an issue with any of the wheel speed sensors. When the left front wheel sensor malfunctions, the light serves as an immediate warning to have your ABS checked.
2. Check Engine Light (CEL) Activation
Although primarily linked to engine issues, sometimes the Check Engine Light may activate when the ABS module communicates a sensor problem to the main ECU. A diagnostic scan tool will confirm if it relates to the C1232 code.
3. Reduced Braking Performance
With a faulty wheel speed sensor, ABS might not function properly. During sudden braking, you may experience longer stopping distances, lack of traction control, or skidding, increasing the risk of accidents.
4. Traction Control Light On
Some modern vehicles will illuminate the Traction Control System (TCS) warning light if wheel speed discrepancies are detected. Since TCS relies heavily on accurate speed readings, a C1232 fault disrupts its performance.
5. Strange Noises from the Front Wheel
You may hear grinding, clicking, or knocking noises from the left front wheel area if the tone ring or sensor is physically damaged, indicating mechanical failure needing urgent attention.
6. Unstable Vehicle Handling
Inconsistent wheel speed readings lead to poor vehicle handling. You might feel the vehicle pulling to one side, especially during acceleration or braking, making driving difficult and unsafe.
How to Diagnose and Repair the C1232 Code
Proper diagnosis ensures correct repairs and avoids unnecessary part replacements. Here is a step-by-step guide:
1. Scan the Vehicle with an OBD-II Scanner
Use a quality OBD-II scanner to retrieve error codes. Confirm that C1232 is present and check for additional related codes. This will help narrow down the root cause.

2. Perform a Visual Inspection
Check the wheel speed sensor wiring, connectors, and tone ring visually. Look for signs of corrosion, disconnection, or physical damage.
3. Test the Wheel Speed Sensor
Use a multimeter to check sensor resistance. A faulty sensor typically shows infinite resistance (open circuit) or values outside manufacturer specifications.
4. Check the Tone Ring
Inspect the tone ring for cracks, missing teeth, or rust buildup. Clean or replace it if necessary to ensure accurate signal generation.
5. Inspect the ABS Control Module
If sensors and wiring are intact, consider checking the ABS module. Some vehicles require specialized tools or dealership assistance for module testing.
6. Confirm Proper Tire Sizes and Inflation
Ensure that all tires are of identical size and properly inflated. Differences can cause incorrect speed readings.
7. Repair or Replace Components as Needed
Based on diagnostic findings, repair wiring, replace damaged sensors, or fix ABS module issues. Always reset the code using the scanner after repairs.
8. Test Drive the Vehicle
Finally, take a test drive and monitor wheel speeds using the scanner. Ensure that the ABS and other warning lights stay off and that the vehicle handles normally.
Cost to Repair the C1232 Code
Repair costs can vary significantly depending on the specific issue:
- Wheel Speed Sensor Replacement: $75–$250
- Wiring Repair: $50–$200
- ABS Module Replacement: $500–$1500
- Labor Charges: $75–$150 per hour
Luxury vehicles or those requiring dealer-only parts may incur higher costs. Early diagnosis and preventive maintenance can keep repair costs manageable.
Conclusion
The C1232 code is a serious warning indicating a malfunction in the left front wheel speed sensor circuit. Ignoring this code can result in degraded ABS performance, poor vehicle control, and increased risk of accidents. Proper maintenance, early diagnosis using an OBD-II scanner, and timely professional repairs are key to resolving this issue. By addressing the problem promptly, you can maintain vehicle safety, enhance driving comfort, and avoid costly repairs in the future. Always prioritize regular vehicle inspections to catch such issues early and ensure safe driving every time you hit the road.
Meet our professional car mechanic, Russell D. Steele, who has been in this field for five consecutive years and works with several automotive companies. He completed the "AUTOMOTIVE & LIGHT DUTY DIESEL TECHNOLOGY" course from NorthWest Lowa Community College, where he learned essential diagnostic and transportation management skills and became a certified mechanic.

1 thought on “C1232 Code: How to Fix The Left Front Wheel Speed Circuit Issue?”
The code came on and it was the c1232 took it to have it checked at an Auto Zone just to see what it meant and it was at the speed sensor circuit that was shorted or circuit open took it to a mechanic and he scanned it there was no codes in the system had new axel shaft put in because during the shaking of left front wheel it damaged the axel was repaired but still have some shaking throughout my car have unplugged the abs control module and still have trembling and does not ride well, what can we do to find the problem and fix it?