Last Updated on May 21, 2025
The U0001 code is one of the more complex OBD2 trouble codes that vehicle owners might encounter. This diagnostic code specifically refers to an issue with the Controller Area Network (CAN) bus—a critical system that allows various modules in your car to communicate effectively. Whether you drive a Dodge, Ford, Toyota, or any other modern vehicle, understanding the meaning, causes, and fixes for the U0001 code can save you time, money, and stress.
In this comprehensive guide, we’ll break everything down in 5 structured parts so you can easily follow along:
What is the U0001 Code?
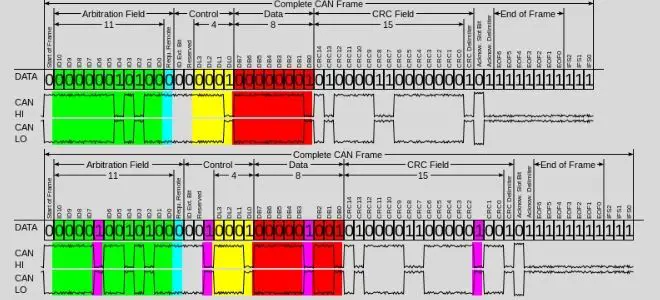
The U0001 code stands for “High-Speed CAN Communication Bus” malfunction. This communication bus system is like the nervous system of your vehicle—it connects the control modules such as:
- Engine Control Module (ECM)
- Transmission Control Module (TCM)
- Anti-lock Braking System (ABS)
- Air Conditioning Module
- Suspension System
- And many others.
When a vehicle displays the U0001 code, it typically means there’s a disruption in CAN High (CAN H) data flow. In other words, these modules are unable to “talk” to each other properly.
🔗 Want to understand more trouble codes? Visit our full OBD2 Code List.
The Role of the CAN Bus System
Before diving into the causes and symptoms, let’s understand the CAN bus itself. The Controller Area Network (CAN) is a robust vehicle bus standard designed to allow microcontrollers and devices to communicate with each other within a vehicle without a host computer. It is divided into two lines:
- CAN High (CAN H) – Operates at 500 kbps
- CAN Low (CAN L) – Operates at 125 kbps
These two lines create a dual-wire system that ensures data transmission even in harsh automotive environments. If either line is damaged or disrupted, it can trigger communication errors like the U0001 fault code.
CAN Bus and Your Vehicle’s Functions
Here’s how important the CAN bus system is:
- Sends commands to engage or disengage traction control
- Transmits data to the dashboard and infotainment systems
- Enables smooth operation of climate control and AC systems
- Coordinates actions between the engine and transmission
A fault in this system means modules may not be receiving or sending accurate information—resulting in performance issues or component failures.
Common Symptoms of the U0001 Code
When your vehicle’s onboard diagnostics system detects the U0001 code, it typically comes with certain warning signs. Recognizing these symptoms early can help you act quickly and prevent deeper issues.
1. Check Engine Light Illuminates
The most obvious sign is the check engine light turning on. This is the ECU’s way of telling you that something’s wrong with the communication network.
2. Difficulty Starting the Vehicle
You might notice your car is slow to start or doesn’t start at all. A disrupted CAN bus means the engine control module may not get the correct signals from other modules like the ignition system.
3. Faulty AC Performance
Since the HVAC system relies on proper data from other modules, you may notice that your AC stops working. This is a typical result of a CAN communication fault.
4. Inconsistent Dashboard Readings
You might experience weird or delayed readings from your dashboard, such as speedometer, fuel level, or warning lights behaving erratically.
5. Additional Trouble Codes
Sometimes, the U0001 code is accompanied by sub-codes such as U0001-88, U0001-87, etc. These indicate specific modules or components that are failing to communicate.
🔧 You may also want to explore related error codes like the U3000 code, which refers to issues within the control module itself.
Other Notable Symptoms:
- ABS or traction control malfunctions
- Steering issues
- Transmission shifting problems
- Vehicle goes into limp mode
Diagnosing the U0001 Code – Step-by-Step Process
Diagnosing the U0001 code requires a structured approach, as communication issues in the CAN bus system can originate from various causes—wiring faults, faulty control modules, or even weak battery voltage. Let’s break down how to accurately identify the root of the problem using industry-recommended practices.
Step 1: Confirm the Fault Code
The first thing you need is an OBD2 scanner capable of reading manufacturer-specific U-codes. Not all basic scanners will pick up the U0001 code or its sub-codes.
- Plug the scanner into your vehicle’s OBD2 port
- Retrieve all current trouble codes
- Note any additional U-codes or B-codes that appear
🔗 Learn how to test your car battery with a multimeter to ensure voltage issues aren’t misleading your diagnostics.
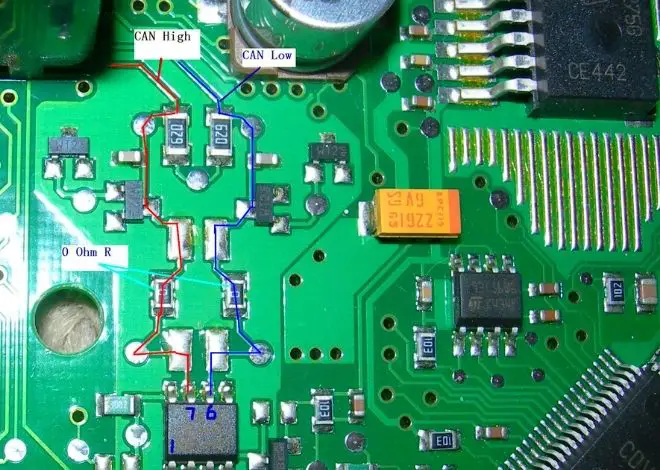
Step 2: Visually Inspect the CAN Bus Wiring
Once the U0001 code is confirmed, begin a visual inspection of all CAN wiring and connectors.
- Look for damaged, frayed, or pinched wires
- Check for loose connectors or corroded terminals
- Examine areas near high heat sources or moving components, where wires may have rubbed or melted
Make sure to inspect both CAN High and CAN Low lines throughout the vehicle. A problem in just one segment of the CAN network can trigger a total communication failure.
Step 3: Check for Low Battery or Charging System Issues
Low voltage from a dying battery or alternator failure can interfere with the CAN bus operation and falsely trigger the U0001 code.
Use a multimeter to measure battery voltage:
- With engine off: Voltage should be around 12.6V
- With engine running: Voltage should be 13.8V to 14.5V
If the battery voltage is significantly lower, it’s advisable to test the battery or charging system before proceeding further.
🔗 See our full guide on blown fuse symptoms that may affect communication lines.
Step 4: Perform a Hard Reset
Before jumping into repairs, try resetting the code:
- Clear the U0001 code with the OBD2 scanner.
- Start the engine and test drive the vehicle for a few minutes.
- Scan again to check if the code reappears.
If the code doesn’t return, it could have been a temporary glitch or low voltage issue.
Step 5: Test CAN Bus Resistance
Using a digital multimeter, perform a resistance test on the CAN bus. Here’s how:
- Turn off the ignition and disconnect the battery.
- Locate the CAN H and CAN L pins on the OBD2 connector (usually pins 6 and 14).
- Measure the resistance across these pins.
You should get a reading of approximately 60 ohms. If you get 120 ohms or infinite resistance, it indicates a faulty termination resistor or open circuit in the CAN bus.
Step 6: Consult Technical Service Bulletins (TSBs)
Manufacturers often issue Technical Service Bulletins (TSBs) when known problems like U0001 occur in specific models. These bulletins provide detailed instructions for:
- Wiring harness repairs
- Module replacements
- Software updates
Search for TSBs using your vehicle’s make, model, and year to ensure the issue hasn’t already been addressed by the manufacturer.
🔗 Learn more about freeze frame data and how it helps with pinpointing vehicle diagnostics.
Step 7: Module Testing and Advanced Diagnostics
If all else fails, a certified technician may need to use advanced scan tools to test each control module’s ability to communicate.
- A failed Body Control Module (BCM), Powertrain Control Module (PCM), or Transmission Control Module (TCM) can cut off network communication.
- Faulty modules can often be isolated by using a breakout box or oscilloscope to trace communication patterns.
🛠️ Proper diagnosis of the U0001 fault code can be complex—but skipping steps may lead to misdiagnosis and wasted repair costs. Follow every step thoroughly for the most accurate results.
How to Fix the U0001 Code – Actionable Repair Solutions
Once you’ve diagnosed the U0001 code and pinpointed its cause—whether it’s damaged wiring, poor voltage, or a failed module—it’s time to take the next step: fixing the issue. This section walks you through all possible repair methods, from basic DIY fixes to more advanced solutions requiring professional tools and support.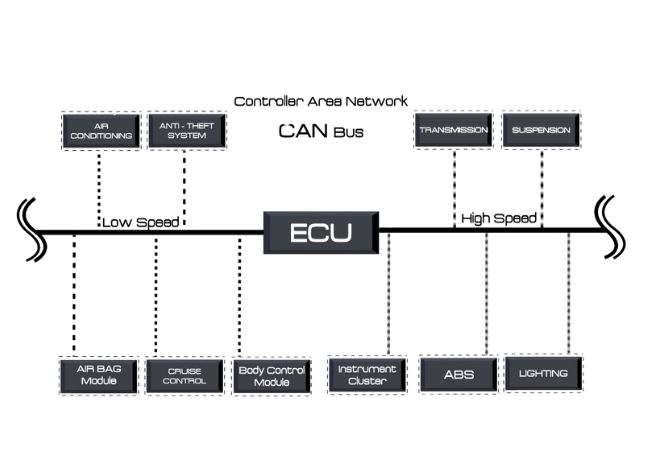
1. Repair or Replace Damaged CAN Bus Wiring
The most common cause of a U0001 fault is damaged or shorted CAN High wiring.
Fix It:
- Locate the damaged portion of the wire.
- Use high-quality automotive wire splices, heat-shrink tubing, and soldering tools to make a clean repair.
- In some cases, it’s safer to replace the entire wire segment if it’s heavily corroded or brittle.
⚠️ Tip: Always disconnect the vehicle battery before performing electrical work to avoid short circuits.
2. Clean or Replace Faulty Connectors
CAN bus connectors may be loose, corroded, or contaminated by moisture, leading to poor communication.
Fix It:
- Remove the connectors and clean them with electrical contact cleaner.
- Check for bent or broken pins and realign them carefully.
- Replace the connector if the pins are damaged or if it doesn’t seat properly.
🔗 Learn about common car electrical faults that might also contribute to this error.
3. Inspect and Test the Control Modules
If wiring and connectors are fine, one or more control modules may have failed. The U0001 code often appears alongside module-specific sub-codes, helping you pinpoint the module that isn’t responding.
Fix It:
- Test modules with a bi-directional scan tool to ensure they’re communicating.
- Replace any module that shows complete communication failure.
- After replacement, reprogram the new module using OEM tools or take the vehicle to a dealer or professional technician for proper calibration.
4. Replace or Repair the CAN Bus Gateway
The gateway module is responsible for routing communication between high-speed and low-speed CAN networks. A fault in this gateway can halt communication and trigger the U0001 code.
Fix It:
- Locate the gateway (often near the fuse box or BCM).
- Perform continuity and voltage tests on the incoming and outgoing CAN lines.
- If no signal passes through, replace the gateway module.
5. Check Battery Health and Charging System
As discussed in Part 3, low voltage can cause false CAN communication errors. Ensure your battery and alternator are functioning properly.
Fix It:
- Replace weak or dying batteries.
- Repair or replace failing alternators.
- Clean battery terminals and apply dielectric grease to prevent future corrosion.
🔗 Need help checking the battery? Read our detailed guide on how to test your car battery.
6. Update the Vehicle’s Software
Some U0001 errors stem from software bugs in the control modules. Car manufacturers release software updates through Technical Service Bulletins (TSBs) to correct these issues.
Fix It:
- Visit your dealership or authorized repair center.
- Request a control module reflash or software update.
- This is especially important if you’ve recently had electrical work or module replacement done.
7. Follow Manufacturer-Specific Repair Procedures
Certain makes and models have known CAN bus issues, and manufacturers provide repair protocols through service manuals or TSBs.
Fix It:
- Search the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA) or your vehicle’s OEM website for relevant bulletins.
- Use factory-recommended parts and follow wiring diagrams accurately.
Bonus Tip: Use a Breakout Box for Advanced Testing
A CAN bus breakout box allows advanced technicians to isolate each line and verify proper voltage and resistance between modules. If you’re still struggling to find the fault, this tool can speed up diagnostics considerably.
✅ Fixing the U0001 code is about following the evidence—starting with wiring and connectors, then moving to voltage checks, and finally module testing or replacement. Don’t guess; test each component in order to avoid wasting money on unnecessary repairs.
Preventing the U0001 Code
By now, you’ve learned what the U0001 code is, its causes, symptoms, diagnostic steps, and repair strategies. But as with most automotive issues, prevention is better than cure. In this final section, we’ll explore how to prevent CAN bus communication failures and offer final thoughts to help you stay ahead of this fault.
How to Prevent U0001 Code Issues
Taking good care of your vehicle’s electrical and communication systems goes a long way in avoiding U-codes. Here’s how to prevent this issue:
1. Maintain Battery and Charging System Health
A weak battery or alternator can cause a voltage drop, which interferes with CAN communication and causes the U0001 code to appear.
- Regularly test your battery using a multimeter.
- Replace old batteries after 3–5 years of use.
- Inspect alternator belts and connections.
🔗 Learn more: Test Your Car Battery with a Multimeter
2. Inspect Wiring During Routine Maintenance
During oil changes or regular inspections, do a quick visual check of wiring harnesses—especially in high-temperature zones like near the engine or transmission.
- Ensure wires aren’t frayed, cracked, or rubbing against hot components.
- Use protective tubing or heat-resistant wraps to prevent future damage.
3. Use OEM Parts and Avoid Poor-Quality Replacements
Always use OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer) wiring, connectors, and modules when replacing components. Low-quality aftermarket parts may lack proper shielding and can degrade CAN communication over time.
4. Avoid Jump-Starting with Incorrect Polarity
Incorrect jump-starting is a common cause of burned modules and CAN network failure. Always:
- Match polarity correctly.
- Use a surge protector jump starter, if available.
- Avoid starting assistance from unknown or poorly maintained batteries.
5. Stay Updated with TSBs and Recalls
Technical Service Bulletins (TSBs) and manufacturer recalls often address CAN bus issues for specific makes and models. Regularly check for updates, especially if your vehicle is showing communication-related issues.
🔗 Also explore: Symptoms of a Bad Starter – which may overlap with U0001 issues if the module isn’t communicating properly.
What Happens If You Ignore the U0001 Code?
Ignoring the U0001 code can have long-term consequences, including:
- Gradual failure of engine or transmission communication
- Airbag or ABS systems becoming non-functional
- Loss of traction control or safety features
- Increased fuel consumption and reduced efficiency
- Costlier repairs down the road as multiple modules get affected
Even if your vehicle appears to run normally at first, CAN communication issues tend to escalate over time.
Final Thoughts: What You Should Remember
Let’s recap the most important things about the U0001 code:
- It means a High-Speed CAN Bus Communication issue.
- It’s often caused by damaged wiring, corroded connectors, weak battery voltage, or a failed control module.
- Symptoms range from a check engine light to AC issues, starting problems, and random dashboard errors.
- You can diagnose it using an OBD2 scanner, visual inspections, voltage tests, and CAN bus resistance checks.
- Most importantly, you can fix it—and even prevent it—by following the correct process and maintaining your vehicle’s electrical system.
🔗 Related topic: What is Freeze Frame Data – use it to capture a snapshot of what was happening when the U0001 code appeared.
Final Verdict on the U0001 Code
The U0001 code may seem intimidating, but with the right tools and a clear step-by-step strategy, it’s absolutely manageable. Whether you’re a DIY enthusiast or taking your vehicle to a professional, understanding this fault code puts you in control. Don’t ignore it—address it early, and your vehicle will thank you with improved reliability, performance, and safety.
✅ Need help with another OBD2 code or electrical fault?
Browse our latest articles at The Effective Guide or explore our growing library of vehicle diagnostics and repair guides.
Kevin Nicholas is an automotive technician who is a genius at software and hardware-related issues. He manually tested more than a hundred OBD scanners and gave his honest opinion on whether the device was worth the money or not. His in-depth OBD review articles help people choose the right product, whether it is a European, American, or Asian vehicle. He completed his Automotive Specialized Training Course at Universal Technical Institute and has more than 15 years of experience in the field.
